Bone Health are vital for overall well-being and mobility. They provide structural support, protect organs, and facilitate movement. Maintaining optimal bone health is essential throughout life, and nutrition plays a pivotal role in achieving this. Bone health is crucial for overall well-being and mobility.
serving as a protective shield for vital organs and enabling movement and physical activity. Maintaining optimal bone health is essential throughout life, from infancy to old age. Nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K, magnesium, and protein are essential for bone formation, maintenance, and repair.
A balanced diet rich in these nutrients can support bone health throughout life and mitigate the risk of bone-related conditions like osteoporosis and fractures. Lifestyle factors like exercise and habits can also promote strong bones. Understanding the power of proper nutrition for bone health can help individuals take proactive steps to safeguard their skeletal well-being.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Bone Structure
- 2 The Role of Nutrition in Bone health
- 3 Foods for Stronger Bones
- 4 Lifestyle Factors Affecting Bone health
- 5 Bone health Across Different Life Stages
- 6 Common Bone health Concerns
- 7 Benefits of Proper Nutrition for Bones health
- 8 Strategies for Maintaining Bones
- 9 Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies
- 10 Practical Tips for Improving Bone health
- 11 Debunking Myths Surrounding Bone health
- 12 Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
- 13 Case Studies and Success Stories
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 FAQs
Understanding Bone Structure
Bones are made up of collagen, a protein framework, and minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which provide strength and density. Bone tissue undergoes constant remodeling, with old bone being replaced by new bone. Bone density refers to the amount of mineral content within bones, influencing their strength and resilience. Bones are complex structures that provide the framework for our bodies and support various physiological functions.
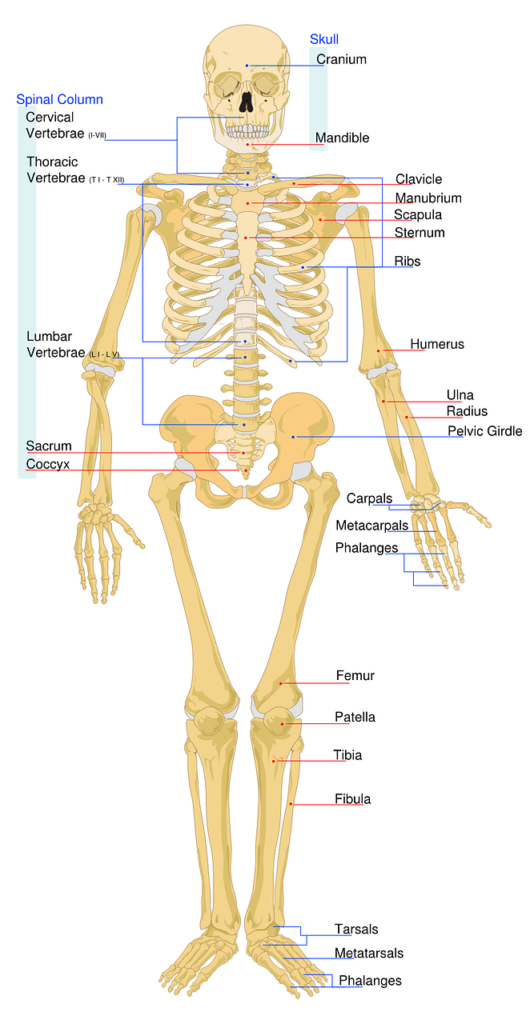
They are composed of collagen, a protein framework, and minerals like calcium and phosphorus, providing strength and density. Collagen fibers deposit calcium hydroxyapatite, which enhances bone hardness and rigidity. Bone tissue undergoes continuous remodeling, with osteoblasts and osteoclasts synthesizing new bone tissue and breaking down old or damaged tissue. Bone mineral density (BMD) is a crucial determinant of strength and resilience. Factors like genetics, age, hormonal fluctuations, and lifestyle habits influence bone density and remodeling processes. Adequate nutrition and regular exercise are essential for bone health.
The Role of Nutrition in Bone health
Proper nutrition is crucial for supporting bone growth, maintenance, and repair. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients that contribute to bone health, including calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K, magnesium, and protein. These nutrients aid in bone formation, mineralization, and remodeling processes
- Calcium: Calcium is a primary mineral component of bones, accounting for their hardness and density. Adequate calcium intake is essential for bone mineralization, where calcium salts are deposited within the bone matrix, contributing to its strength and rigidity. Without sufficient calcium, bones may become weak and prone to fractures.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and utilization. It helps regulate calcium levels in the blood and promotes the deposition of calcium into bones. Exposure to sunlight triggers the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, while dietary sources such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements can also contribute to vitamin D intake.
- Vitamin K: Vitamin K is involved in the synthesis of proteins necessary for bone mineralization. It helps activate osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium ions to the bone matrix, enhancing bone strength and density. Green leafy vegetables, such as kale, spinach, and broccoli, are excellent sources of vitamin K.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is another essential mineral that supports bone health. It plays a role in bone mineralization and regulates the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone formation and resorption, respectively. Nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy greens are rich sources of magnesium.
- Protein: Protein is a fundamental building block of bones, comprising approximately 50% of bone volume. It provides the structural framework for bone tissue and supports the repair and remodeling processes. Including sources of high-quality protein, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and tofu, in the diet is essential for maintaining bone health.
These essential nutrients work synergistically to support bone formation, mineralization, and remodeling processes. Calcium provides the structural foundation, while vitamin D facilitates its absorption and utilization. Vitamin K activates proteins involved in bone mineralization, magnesium regulates bone cell activity, and protein provides the structural framework for bone tissue.
Incorporating a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods into the diet ensures a comprehensive supply of these essential nutrients, promoting optimal bone health and reducing the risk of bone-related conditions such as osteoporosis and fractures. By prioritizing proper nutrition, individuals can support the structural integrity and resilience of their bones, enabling them to maintain mobility, strength, and overall well-being throughout life.
Foods for Stronger Bones
Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods is key to promoting strong and healthy bones. Calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods contribute to bone strength. Additionally, vitamin D sources like fatty fish, egg yolks, and sunlight exposure facilitate calcium absorption. Other nutrients such as vitamin K from leafy greens and magnesium from nuts and seeds also support bone health. A well-rounded, nutrient-rich diet is crucial for promoting strong and healthy bones.
Calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods, are essential for maintaining optimal bone health. Vitamin D, found in fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, plays a vital role in calcium absorption and utilization. Vitamin K, found in leafy green vegetables, helps regulate calcium metabolism and support bone health. Magnesium, found in nuts, seeds, and whole grains, is essential for bone metabolism and enzyme activation. By incorporating these foods into the diet, individuals can ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients that support bone health. By prioritizing these foods, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain strong and healthy bones throughout life.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Bone health
In addition to nutrition, lifestyle choices significantly impact bone health. Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing and resistance activities, helps build and maintain bone density. Conversely, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and sedentary behavior can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures.
Bone health is influenced by various lifestyle factors, including nutrition, physical activity, and habits. Regular exercise is crucial for promoting bone health, as it stimulates bone formation and increases bone density. Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, dancing, and hiking stimulate bone formation, while resistance exercises like weightlifting and resistance band workouts build muscle strength and promote bone growth. These exercises can enhance bone density, reduce the risk of osteoporosis, and improve overall bone health.
However, certain lifestyle habits can have detrimental effects on bone health. Smoking, for example, can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures due to its chemicals. Excessive alcohol consumption can also negatively impact bone health, disrupting calcium absorption and metabolism, and weakening bones over time. Limiting alcohol intake to moderate levels can help preserve bone health and reduce fracture risk. Sedentary behavior, such as prolonged sitting or lack of physical activity, can contribute to bone loss and decrease bone density.
By prioritizing exercise, avoiding detrimental habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and leading an active lifestyle, individuals can significantly improve their bone health and reduce the risk of fractures and bone-related conditions. Making informed choices regarding lifestyle factors can have long-lasting benefits for skeletal integrity and overall well-being.
Bone health Across Different Life Stages
Bone health requirements vary throughout life. During childhood and adolescence, adequate nutrition is crucial for optimal bone development. In adulthood, maintaining bone density becomes essential to prevent age-related decline. In the elderly population, strategies to prevent osteoporosis and fractures are paramount.
Bone health needs vary across different life stages, reflecting the dynamic nature of skeletal development, maintenance, and aging. Understanding these variations is crucial for implementing appropriate strategies to support bone health at each stage.

During childhood and adolescence, optimal bone development lays the foundation for lifelong skeletal health. Adequate nutrition, particularly calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients, is essential for supporting bone formation and mineralization. Engaging in weight-bearing physical activities and exercises that promote bone loading, such as running, jumping, and sports participation, further enhances bone density and strength.
In adulthood, maintaining bone density becomes increasingly important to prevent age-related decline in skeletal health. Ensuring adequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients remains crucial for supporting bone maintenance and repair. Regular weight-bearing and resistance exercises help preserve bone density and strength, mitigating the effects of age-related bone loss. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy body weight, can further support bone health in adulthood.
In the elderly population, strategies to prevent osteoporosis and fractures become paramount, as age-related bone loss accelerates and the risk of falls and fractures increases. Adequate nutrition, balance and strength exercises, regular screening for osteoporosis, and early intervention, such as medication therapy or lifestyle modifications, may be recommended for individuals at risk of bone-related conditions. Addressing bone health concerns proactively in old age can maintain independence, mobility, and quality of life as individuals age.
Common Bone health Concerns
Osteoporosis, characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, is a prevalent bone health condition, especially among older adults, particularly postmenopausal women. Fractures and injuries resulting from weakened bones are significant concerns, highlighting the importance of preventive measures.
Bone health concerns encompass a range of conditions that affect the integrity and strength of skeletal tissue. Understanding these concerns is essential for implementing preventive measures and promoting optimal bone health.
Osteoporosis is a bone health condition characterized by low bone mass and tissue deterioration, increasing fragility and fracture susceptibility. It primarily affects older adults, especially postmenopausal women, but can also affect men and younger individuals. It often develops silently until a fracture occurs, with common fracture sites being the hip, spine, and wrist. Risk factors include advanced age, female gender, hormonal changes, low body weight, family history, and certain medical conditions. Prevention and management strategies involve promoting bone health through nutrition, weight-bearing exercises, a healthy lifestyle, and medication therapy under medical supervision.
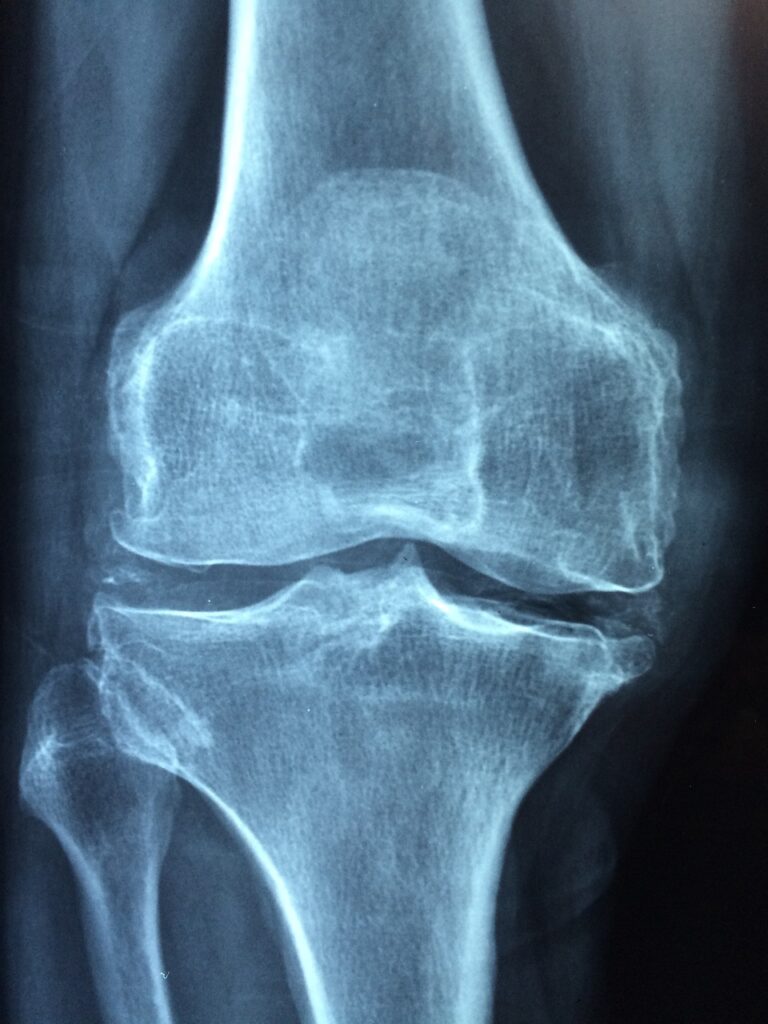
Fractures and Injuries:Poor bone health, particularly in individuals with osteoporosis or low bone density, increases the risk of fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist. These injuries can lead to pain, disability, loss of independence, and reduced quality of life. Preventive measures include ensuring a safe home environment, using assistive devices, and participating in balance and strength exercises. Early detection and management of osteoporosis can also help prevent fractures and minimize their impact on overall health.
Raising awareness about bone health issues like osteoporosis and fractures encourages proactive measures, healthy lifestyle habits, and prevention of complications, promoting lifelong bone strength and resilience.
Benefits of Proper Nutrition for Bones health
A diet rich in essential nutrients supports bone density and strength, reducing the risk of fractures and bone-related conditions. Proper nutrition enhances bone remodeling processes, ensuring optimal bone health throughout life. Proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining optimal bone health throughout life. A diet rich in essential nutrients, such as calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K, magnesium, and protein, supports bone density and strength.
These nutrients are essential for bone metabolism, bone mineralization, and bone strength. A balanced diet can reduce the risk of fractures and bone-related conditions like osteoporosis, which increases the susceptibility to fractures. Additionally, proper nutrition enhances bone remodeling processes, which involve the continuous turnover of old bone tissue and the formation of new bone. By prioritizing a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, individuals can maintain strong and healthy bones throughout life. In conclusion, proper nutrition is essential for promoting bone health, reducing fracture risk, and enhancing bone remodeling processes.
Strategies for Maintaining Bones
Balanced diet recommendations include incorporating calcium-rich foods, vitamin D sources, and other essential nutrients into daily meals. Engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy body weight are integral to preserving bone health.
Bone health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being and can be maintained through a multifaceted approach. It involves a balanced diet, regular physical activity, avoiding harmful habits, and maintaining a healthy body weight. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients for bone formation, maintenance, and repair, while regular physical activity stimulates bone formation and increases density.
Avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also help maintain optimal bone health. Maintaining a healthy body weight is essential for bone health, as being underweight or overweight can negatively impact bone density and increase the risk of fractures. By implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve bone health and reduce the risk of fractures and bone-related conditions.
Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies
In cases of nutritional deficiencies or specific dietary needs, supplements may be recommended under healthcare professional guidance. Regular monitoring and adjustments to dietary and lifestyle habits are essential for addressing individual needs and optimizing bone health.
Nutritional deficiencies can be addressed through the guidance of healthcare professionals, who can assess individual needs, conduct tests, and recommend suitable supplements based on specific deficiencies or dietary restrictions. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure safety, efficacy, and proper dosage.
Regular monitoring and adjustments are crucial for identifying deficiencies and assessing the effectiveness of interventions. Healthcare professionals may recommend periodic blood tests or bone density scans to evaluate bone health and monitor changes over time. Based on these results, adjustments to dietary and supplementation regimens may be made to optimize bone health.
An individualized approach is essential, considering factors such as age, gender, medical history, dietary preferences, and lifestyle habits. Tailoring interventions to meet individual needs ensures that deficiencies are adequately addressed and optimal bone health is promoted. Regular communication and collaboration between individuals and healthcare professionals facilitate effective management of nutritional deficiencies and support long-term bone health goals.
By addressing nutritional deficiencies through supplementation under healthcare professional guidance, along with regular monitoring and adjustments to dietary and lifestyle habits, individuals can optimize bone health and reduce the risk of bone-related complications. Prioritizing individualized care and proactive management of nutritional needs are essential for promoting skeletal integrity and overall well-being.
Practical Tips for Improving Bone health
Practical strategies include meal planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake, incorporating bone-strengthening exercises into fitness routines, and establishing habits conducive to overall well-being. Small, sustainable changes can have significant long-term benefits for bone health.
Improving bone health involves incorporating practical strategies into daily routines that support optimal bone density and strength. By adopting small, sustainable changes, individuals can promote skeletal integrity and reduce the risk of fractures and bone-related conditions. Here are some practical tips for enhancing bone health:
1. Plan meals rich in essential nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K, magnesium, and protein, including a variety of foods from different food groups. Incorporate nutrient-dense ingredients into meals to ensure adequate intake of key nutrients that support bone density and strength.
2. Incorporate bone-strengthening exercises into your fitness routine to promote bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, dancing, and stair climbing, stimulate bone formation and increase bone density. Resistance exercises, like weightlifting, resistance band workouts, and bodyweight exercises, further enhance bone strength and promote skeletal integrity.
3. Establish habits conducive to overall well-being, such as getting adequate sleep each night, managing stress through relaxation techniques, avoiding harmful habits, maintaining a healthy body weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity, and prioritizing small, sustainable changes. Set achievable goals and gradually incorporate healthy practices into your lifestyle, celebrating progress and staying motivated by tracking your successes and acknowledging the positive impact of your efforts on bone health.
By implementing these practical tips, individuals can take proactive steps to improve bone health and support skeletal integrity throughout life.
Debunking Myths Surrounding Bone health
Dispelling common myths and misconceptions about bone health is essential for promoting accurate information and encouraging proactive measures. Evidence-based facts provide clarity and empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their bone health.
Addressing common myths and misconceptions about bone health is crucial for promoting accurate information and empowering individuals to take proactive measures to support skeletal integrity. Factors such as aging, lifestyle factors, nutrition, physical activity, and habits influence bone health throughout life.
1. Calcium supplements alone are sufficient for strong bones. Calcium is just one of many nutrients necessary for maintaining optimal skeletal integrity. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is key to supporting bone health. Supplements may be recommended under healthcare professional guidance in cases of deficiencies.
2. Drinking milk is the only way to get sufficient calcium. While dairy products are a rich source of calcium, leafy green vegetables, fortified foods like tofu, and plant-based milk alternatives also provide significant amounts of calcium. Incorporating other calcium-rich foods into the diet can help meet calcium needs.
3. Bone health is predetermined and cannot be improved. Genetics play a role in determining bone density and structure, but lifestyle factors such as nutrition, physical activity, and habits significantly influence bone health. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular weight-bearing and resistance exercises, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can help optimize bone health and reduce the risk of fractures.
5. Osteoporosis only affects women, particularly postmenopausal women due to hormonal changes. Men can also experience age-related bone loss and develop osteoporosis, especially with factors such as low testosterone levels, certain medications, and lifestyle habits. By debunking these myths and providing evidence-based facts, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of the factors influencing skeletal integrity and take proactive steps to support their bone health throughout life.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Consulting healthcare professionals, including physicians, dietitians, and other specialists, is valuable for personalized guidance and support. Expert advice helps tailor nutritional and lifestyle recommendations to individual needs, ensuring comprehensive bone health management. Consulting healthcare professionals is crucial for optimizing bone health.

They provide personalized guidance, evidence-based recommendations, comprehensive management, monitoring, and follow-up to individuals. They assess individual factors affecting bone health, such as age, gender, medical history, dietary preferences, and lifestyle habits. They develop tailored plans to address specific concerns, ensuring that recommendations align with individual needs and goals. Healthcare professionals also base their recommendations on scientific research, providing up-to-date information and solutions.
They also coordinate care with other healthcare providers to address underlying medical conditions or concerns that may impact bone health. Regular follow-up appointments and assessments help track changes in bone density, nutritional status, and overall well-being. Consulting healthcare professionals also help mitigate potential risks associated with interventions, ensuring that recommendations are safe and appropriate for individual circumstances.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-life case studies and success stories serve as powerful examples of the transformative impact that adopting healthy habits can have on bone health outcomes. These stories provide inspiration and motivation for individuals to prioritize nutrition, exercise, and overall wellness to achieve optimal bone health.
- Case Study:
Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, was diagnosed with osteopenia, a condition characterized by low bone density, during a routine bone density scan. Concerned about her bone health, Sarah consulted with a healthcare professional who recommended a personalized plan to improve her bone density. With guidance from a dietitian, Sarah modified her diet to include calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, as well as vitamin D sources like fatty fish and sunlight exposure. She also began incorporating weight-bearing exercises such as walking, hiking, and strength training into her weekly routine. Over time, Sarah’s bone density improved, and subsequent bone density scans showed significant increases in bone mineral density, reducing her risk of osteoporosis and fractures. - Success Story:
John, a 60-year-old man, struggled with mobility issues and chronic pain due to osteoporosis-related fractures in his spine and hip. Determined to regain his independence and improve his quality of life, John embarked on a journey to prioritize his bone health. With guidance from a physical therapist and nutritionist, John implemented a comprehensive plan that included regular physical therapy sessions to improve strength, balance, and flexibility, as well as dietary modifications to support bone health. He focused on consuming calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, as well as vitamin D sources like fatty fish and supplements as recommended by his healthcare professional. Through consistent effort and dedication, John experienced significant improvements in his bone health, mobility, and overall well-being. He regained his independence, resumed activities he once enjoyed, and felt empowered to take control of his bone health.
These case studies and success stories highlight the transformative impact of adopting healthy habits on bone health outcomes. By sharing real-life examples of individuals who have successfully improved their bone health through nutrition, exercise, and overall wellness, we can inspire and motivate others to prioritize their own bone health. Through personalized guidance, evidence-based recommendations, and ongoing support from healthcare professionals, individuals can achieve optimal bone health and lead fulfilling, active lives.
Conclusion
Proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining strong bones throughout life. Nutrient-dense foods, consistent physical activity, and bone-friendly lifestyle practices help protect against bone-related ailments and promote overall well-being. Essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein are essential for fortifying bone density and structure.
Consuming calcium-rich foods like dairy products and leafy greens, along with vitamin D sources like fatty fish and sunlight exposure, can strengthen skeletal integrity and reduce the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises and resistance training, stimulates bone formation and enhances bone density. Habits that promote overall well-being, such as adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol, can also contribute to optimal bone health.
The journey to maintain strong bones is multifaceted and requires a holistic approach that includes nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle choices. By embracing these principles and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals can nurture their bones and safeguard against bone-related conditions, enhancing their quality of life and promoting longevity. Prioritizing bone health is essential for overall wellness and a vibrant, fulfilling life.
FAQs
- How does nutrition affect bone health?
Proper nutrition provides essential nutrients necessary for bone formation, mineralization, and remodeling, ensuring optimal bone strength and density. - What are the best foods for bone health?
Calcium-rich foods like dairy products and leafy greens, vitamin D sources such as fatty fish and sunlight exposure, and other nutrients like vitamin K and magnesium contribute to bone health. - Why is exercise important for bone health?
Weight-bearing and resistance exercises stimulate bone remodeling and increase bone density, promoting stronger and healthier bones. - Can supplements help improve bone health?
In cases of nutrient deficiencies or specific dietary needs, supplements may be beneficial under the guidance of healthcare professionals to support bone health. - How can individuals prevent osteoporosis and fractures?
By maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding detrimental habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.

