Is fish oil or flax seeds a better source of the well-known omega-3 fatty acids that are creating waves in the health world for all kinds of reasons? Now let’s investigate.
In today’s health-conscious world, people are increasingly incorporating natural sources of nutrients like flaxseed, fish oils, and nuts into their diets. Flaxseed is known for its high nutrient profile, including fiber, protein, and essential fatty acids, particularly Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is known for its heart-healthy properties. ALA helps lower LDL cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Fish oils, rich in Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), play crucial roles in brain health, inflammation regulation, and cardiovascular support.
Incorporating fish oils into one’s diet can significantly contribute to meeting the body’s Omega-3 requirements and promoting heart health. Nuts, while not as high in ALA, offer numerous nutritional benefits, including healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Some nuts, like walnuts and almonds, contain significant amounts of ALA, further enhancing their cardiovascular benefits. Regular consumption of nuts has been associated with improved heart health and weight management. Understanding the advantages of flaxseed, fish oils, and nuts in cholesterol management and Omega-3 content can help individuals make informed dietary choices to support their overall health and well-being.
Contents
- 1 Flaxseed: A Nutritional Powerhouse
- 2 Fish Oils: The Omega-3 Source
- 3 Nuts: Another Source of Healthy Fats
- 4 Comparative Analysis
- 5 Considerations for Consumption
- 6 uses of flaxseed oil and other omega-3 fatty acids
- 7 Heart health
- 8 Inflammatory Disorders
- 9 Brain Health
- 10 Mental Health
- 11 Eye Health
- 12 Dietry source
- 13 Available Forms
- 14 How to take it
- 15 Conclusion
- 16 FAQs
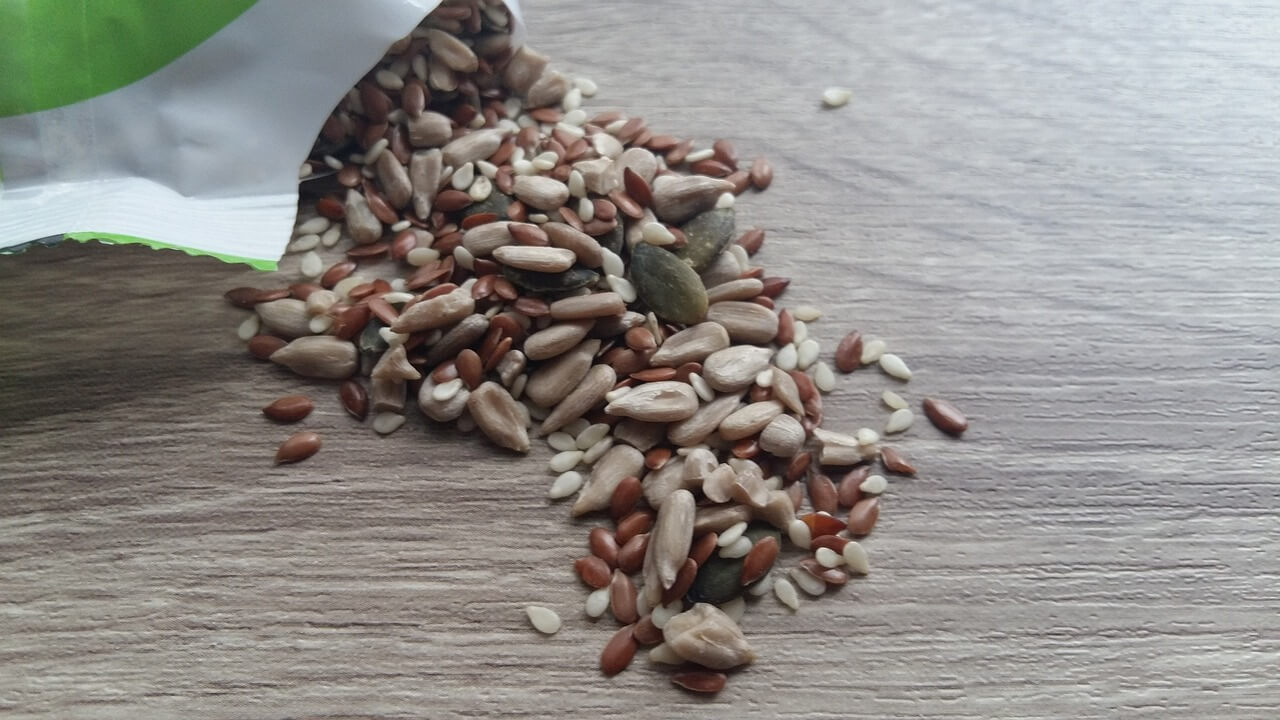
Flaxseed: A Nutritional Powerhouse
Flaxseed, also referred to as linseed, is celebrated for its remarkable nutrient composition. It is abundant in essential nutrients such as fiber, protein, and beneficial fatty acids, making it a standout in terms of nutrition. However, what truly sets flaxseed apart is its high content of Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a specific type of Omega-3 fatty acid.
ALA is recognized for its positive impact on heart health. Numerous studies have demonstrated its ability to reduce cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, commonly known as the “bad” cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular ailments. By incorporating flaxseed into one’s diet, individuals can harness the benefits of ALA to support cardiovascular health and potentially lower their risk of heart-related issues.

The mechanism behind ALA’s cholesterol-lowering effects involves its ability to reduce inflammation and promote the removal of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. Additionally, ALA may help improve the function of blood vessels, further supporting heart health. Including flaxseed in various forms, such as ground seeds, oil, or flour, in meals and snacks can be an effective way to boost ALA intake and reap its cardiovascular benefits.
Overall, flaxseed’s richness in ALA makes it a valuable dietary addition for individuals looking to optimize their heart health and manage cholesterol levels naturally. Incorporating flaxseed into a balanced diet can contribute to overall well-being and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Fish Oils: The Omega-3 Source
Fish oils, derived from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout, are rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids are essential for brain health, inflammation regulation, and cardiovascular health. Adequate intake of EPA and DHA is linked to improved cognitive function, memory retention, and overall brain development. They also have potent anti-inflammatory properties, which help mitigate the risk of chronic inflammation-related health conditions like cardiovascular diseases, arthritis, and certain cancers.
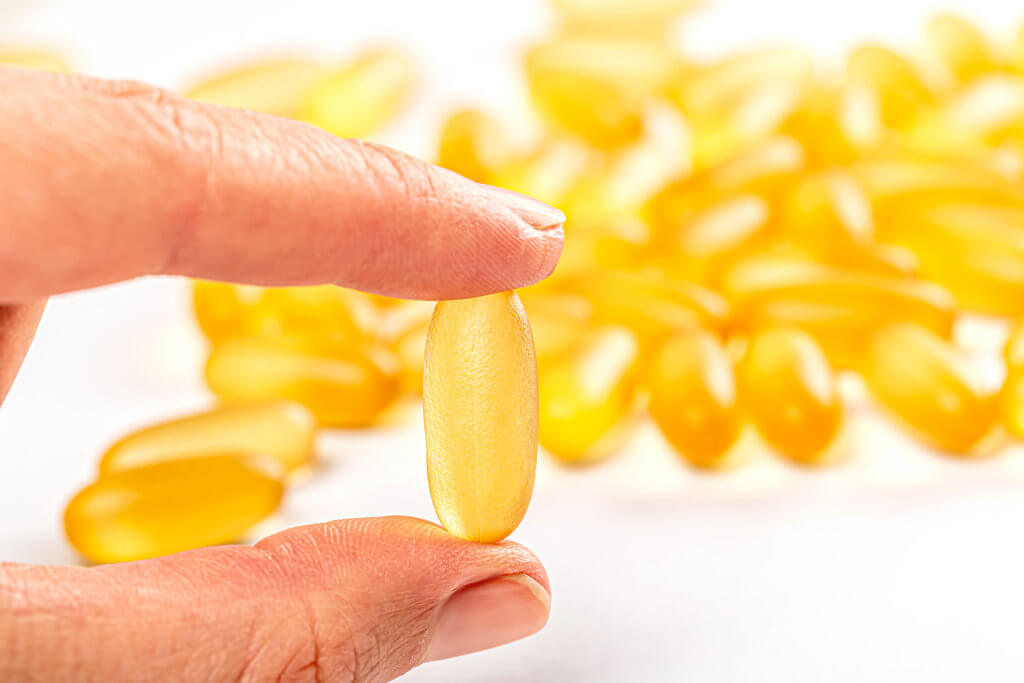

Fish oils are also beneficial for cardiovascular health, as they reduce triglyceride levels, lower blood pressure, and improve blood vessel function. They also prevent blood clot formation, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Fish oil supplements, available in capsules, liquid extracts, and fortified foods, are a convenient alternative to regular fish consumption or dietary restrictions.
In summary, fish oils are highly valued for their high Omega-3 content, particularly EPA and DHA, which play crucial roles in brain function, inflammation regulation, and cardiovascular health. Incorporating fish oils into one’s diet, either through fatty fish consumption or supplements, can provide numerous health benefits and contribute to overall well-being, especially for those with limited access to fish-rich diets.
Nuts: Another Source of Healthy Fats
Nuts, including almonds, walnuts, and cashews, are a popular choice for nutrient-rich snacks due to their high nutritional composition. They are rich in healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals, making them a valuable addition to any diet. Some nuts contain Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of Omega-3 fatty acid that offers health benefits like heart health and inflammation reduction. Nuts also contain fiber, which aids digestion and regulates blood sugar levels, contributing to overall metabolic health.

Regular consumption of nuts has been linked to improved heart health due to their high levels of unsaturated fats, which help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Nuts also contribute to weight management by promoting satiety and reducing cravings. Incorporating nuts into one’s diet can help control appetite and prevent overeating, supporting weight loss or maintenance goals. Overall, nuts contribute to a well-rounded approach to nutrition and promote overall health and well-being.
Comparative Analysis
Flaxseed, fish oils, and nuts are all essential sources of Omega-3 fatty acids, each with their own unique nutritional value and health benefits. Flaxseed is a plant-based source of ALA, which is essential for heart health and reduced cholesterol levels. However, the conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA, the more potent forms found in fish oils, is relatively inefficient in the body.
Despite this, flaxseed remains a valuable dietary addition for those following plant-based diets or seeking alternative sources of Omega-3s. Fish oils, on the other hand, offer EPA and DHA in their ready-to-use forms, providing immediate benefits for cardiovascular health and inflammation reduction. These fatty acids are known for their potent anti-inflammatory properties and support heart function. However, fish oils may not be suitable for vegetarians or those with dietary restrictions. Nuts, while not as rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, offer a variety of other nutrients and health benefits, including improved heart health, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and certain cancers. Incorporating these foods into one’s diet can maximize their nutritional benefits.
Considerations for Consumption
Incorporating flaxseed, fish oils, and nuts into your diet is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Fish oils are not suitable for vegetarians or vegans, while flaxseed and nuts are plant-based alternatives rich in essential nutrients. To incorporate these foods into your diet, add ground flaxseed to smoothies or oatmeal, sprinkle it over yogurt, salads, or baked goods, or sprinkle it over yogurt, salads, or baked goods.
Consuming fatty fish regularly provides EPA and DHA directly from the source, supporting heart health and overall well-being. If you prefer plant-based options, consider algae-based Omega-3 supplements. Nuts are a versatile and tasty addition to your diet, providing healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They can be added to salads, stir-fries, or baked goods for added flavor and texture.
In summary, it’s crucial to consider individual dietary preferences and any restrictions when incorporating these foods into your diet. Whether you choose plant-based options like flaxseed and nuts or fatty fish, there are practical ways to reap the nutritional benefits of these nutrient-rich foods and support your overall health and well-being.
uses of flaxseed oil and other omega-3 fatty acids
Clinical studies suggest that flaxseed oil and other omega-3 fatty acids may help treat a variety of conditions.
Heart health
Flaxseed oil and Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their positive effects on heart health. They help reduce triglyceride levels, which are risk factors for heart disease, and lower blood pressure, particularly in individuals with hypertension. These fats promote vasodilation and reduce vascular resistance, regulating blood pressure and maintaining healthy cardiovascular function.
Omega-3 fatty acids also prevent blood clots, which can block blood flow to the heart or brain, leading to heart attacks or strokes. They inhibit platelet aggregation and reduce blood viscosity, maintaining blood flow and preventing clot formation. They also improve blood vessel function, supporting endothelial cells that promote vasodilation, regulate blood pressure, and prevent inflammation and clot formation.

These fatty acids also have anti-inflammatory effects, which help reduce inflammation in the arterial walls, slowing down the progression of atherosclerosis and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Incorporating Omega-3-rich foods like flaxseed oil into your diet or taking Omega-3 supplements can support cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Inflammatory Disorders
Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, making them beneficial for managing inflammatory disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriasis. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition characterized by joint inflammation, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids can alleviate symptoms and improve outcomes in this condition by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators. This leads to decreased joint pain, improved joint function, and reduced disease activity.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory condition involving chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Omega-3 fatty acids can modulate the inflammatory response and promote intestinal healing, reducing inflammation in the gut, alleviating symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea, and decreasing the risk of disease flare-ups.

Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Inflammation plays a central role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, and omega-3 fatty acids can help alleviate symptoms and improve skin health by suppressing inflammation in the skin and reducing the severity of psoriatic lesions.
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into the diet or taking supplements may offer a natural and effective approach to managing inflammation and promoting overall health and well-being in individuals with inflammatory disorders.
Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, are essential for brain health due to their abundance in the brain’s cell membranes. DHA is crucial for optimal brain development, particularly during fetal development and infancy, as it is a key component of the brain’s gray matter and white matter, which facilitate communication between different regions. Adequate intake of DHA during pregnancy and early childhood is essential for proper brain growth and development.
Clinical studies suggest that DHA may improve cognitive function, including memory, attention, and executive function. It supports synaptic plasticity, which enhances learning and memory processes, leading to improved cognitive performance. DHA also plays a role in mood regulation and emotional well-being, as it plays a role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
Omega-3 fatty acids also exhibit neuroprotective properties, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. DHA maintains the structural integrity of neuronal membranes, protects against oxidative stress and inflammation, and promotes neuronal survival and repair. Regular consumption of Omega-3-rich foods or supplementation with DHA may help support brain health and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Mental Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid), have been shown to have potential therapeutic effects on mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Studies have shown that individuals with depression often have lower levels of EPA in their blood, which can be improved by supplementing with EPA-rich formulations. EPA plays a crucial role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are involved in mood regulation. By increasing these neurotransmitters in the brain, EPA may help alleviate symptoms of depression and improve overall mood.

Anxiety disorders can also be managed by EPA supplementation, which can reduce symptoms of anxiety and promote calmness and relaxation. EPA modulates the activity of neurotransmitter systems involved in anxiety regulation, such as serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) systems. This enhances neurotransmitter function, reducing anxiety symptoms and improving overall mental well-being.
Bipolar disorder, characterized by episodes of depression and mania or hypomania, can be stabilized by EPA supplementation, which can help stabilize mood and reduce the frequency and severity of mood swings. However, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying Omega-3’s effects on mental health and to identify optimal dosages and treatment protocols for different individuals.
Eye Health
DHA, an Omega-3 fatty acid, is crucial for maintaining optimal eye health. It plays a significant role in retinal health, supporting the structural integrity of retinal cells and promoting proper functioning of photoreceptor cells. DHA also helps reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a progressive eye disease that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. DHA’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties protect retinal cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation, which are implicated in AMD development and progression.
Dry eye syndrome, a common condition characterized by insufficient tear production or poor tear quality, is also benefitted by DHA. It reduces inflammation in tear glands and improves tear production and quality. DHA helps maintain the stability of tear film and lubricates the eye surface, alleviating dryness and discomfort associated with dry eye syndrome.
Incorporating Omega-3-rich foods into the diet or taking Omega-3 supplements can help support eye health and reduce the risk of vision-related conditions, particularly in older adults. However, it is essential to consult with an eye care professional before starting any supplementation regimen, especially if you have pre-existing eye conditions or are taking medications.
Overall, clinical studies provide strong evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of flaxseed oil and other Omega-3 fatty acids for a wide range of conditions, including heart disease, inflammatory disorders, brain health, mental health, and eye health. Incorporating Omega-3-rich foods like flaxseed oil into your diet or taking Omega-3 supplements may offer significant health benefits and support overall well-being. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking medications.
Dietry source
Flaxseed oil, derived from the seed of the flax plant, boasts a remarkable Omega-3 fatty acid content, with approximately 50 to 60% consisting of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). Surprisingly, this exceeds the Omega-3 content found in fish oil. However, the body’s conversion of ALA into the beneficial Omega-3 fatty acids, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), typically found in fish oil, is not very efficient. Therefore, while flaxseed oil is rich in ALA, it may not offer the same benefits as EPA and DHA from fish oil.
Available Forms
Flaxseed oil is available in both liquid and softgel capsule forms. Due to its susceptibility to rancidity, proper storage is crucial, and refrigeration is recommended. Quality flaxseed oil products are packaged in dark containers and processed at low temperatures to preserve their integrity and nutritional value. It’s essential to choose supplements from reputable companies that certify their products to be free of heavy metals such as lead and mercury.
How to take it
Determining the appropriate dosage of flaxseed oil depends on various factors, including dietary intake of fatty acids and the specific condition being targeted. For pediatric use, it’s important to consult with a doctor or pediatrician before administering flaxseed oil to children under 18. As for adults, there is no universally recommended dosage, and it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the optimal dose based on individual needs and health considerations.
Typically, flaxseed oil is consumed in liquid form, with approximately 7 grams of ALA per 15 mL (1 tablespoon), providing around 130 calories. However, dosage may vary depending on personal requirements and health goals, highlighting the importance of personalized guidance from a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Flaxseed, fish oils, and nuts are essential components of a healthy diet, each offering unique nutritional benefits. Flaxseed is rich in Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of Omega-3 fatty acid that helps lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Fish oils provide EPA and DHA, which are highly bioavailable forms of Omega-3s,
which are associated with improved heart function and reduced inflammation. Including fish oil supplements in your diet ensures adequate intake of these essential fatty acids. Nuts, on the other hand, offer a diverse array of nutrients, including healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Regular consumption of nuts has been linked to improved heart health, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases. By incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet, you can maximize nutritional benefits and support overall health and well-being. Embracing variety and balance in your diet ensures that you receive the essential nutrients needed to thrive and maintain optimal health for years to come.
FAQs
- Can flaxseed replace fish oils for Omega-3 supplementation? While flaxseed is a valuable source of ALA, it may not fully replace fish oils, as the conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA is limited in the body.
- Are there any risks associated with consuming flaxseed? Flaxseed is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts. However, individuals with certain medical conditions or allergies should exercise caution.
- How much fish oil should I take daily for optimal health benefits? The recommended dosage of fish oil supplements varies depending on individual health needs and considerations. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
- Which nuts are highest in Omega-3 fatty acids? Walnuts and flaxseeds are among the nuts with the highest ALA content, making them excellent choices for increasing Omega-3 intake.
- Is it safe to consume flaxseed, fish oils, and nuts together in one’s diet? Yes, incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet can provide a diverse array of nutrients and health benefits, supporting overall well-being

